The oil inlet and outlet of the line mount valve have internal threads, which are connected to the pipes and other components through the connected pipe joints. There are two-way ports, three-way ports, or more. The pipe valve is the oldest type of installation and connection valve. It has been widely used since the beginning of the last century, and it continues to be used today. The pipe valve is the only independent and complete valve among various installation and connection methods: it can be used after connecting pipe joints and pipes, without any other accessories. As the hydraulic system becomes increasingly complex, the weaknesses of this installation method become increasingly prominent:
1) Components are scattered and occupy a large area;
2) There are many parts that may leak;
3) It is inconvenient to assemble and disassemble.
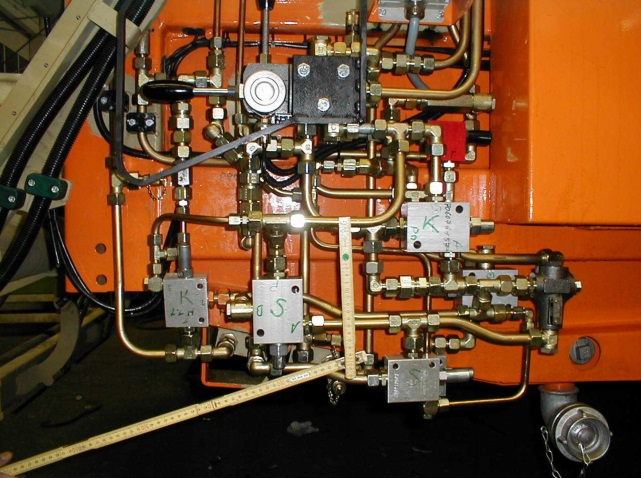


Sectional valves (sectional valves, multiple section directional valves, multiple flow valves) are generally called multi-way valves in China. It is developed from the tubular manual reversing valve: a control section contains a reversing valve spool, which controls a group of actuators-hydraulic cylinders or hydraulic motors. Almost all control functions are concentrated on this one piece. Some multi-way valve slices with different control methods make the positions of the oil inlet P and the oil return port T of each slice the same, so they can be assembled together and share P and T. Multi-way valves generally have a common control block: an oil source block, and generally a tail block. Then fasten together with bolts. The biggest feature of this installation and connection method is flexibility, you can choose as many actuators as you need to control. Because of the common oil source block, the structure is relatively compact. The valve body is mostly made of cast iron, but also made of steel. From the earliest manual development to today, multi-way valves have various control forms such as hydraulic control, electromagnetic valve control, electric proportional valve control, and bus control. If the reliability and cost performance of the electronic control are greatly improved, there is no need for an additional emergency manual. Multi-way valves are widely used in hydraulic systems of mobile machinery. Considering the operating habits, this assembly method will exist for a long time.

Weaknesses of multi-way valves:
There may be leakage between the sheets.
Because the pipe is fixed on the valve body, when replacing a certain piece of valve, not only the fastening bolt must be loosened, but also the pipe must be disassembled. Still more troublesome. This installation connection method began to be crowded out by the integrated block method. Some cartridge valve manufacturers use a specially designed large integrated block instead of a combination of multiple chips for some high-volume hosts. This greatly reduces possible leak sites and the overall overall dimensions can also be reduced. However, this technology needs to break through the following weak links:
(1) The quality of the casting as an integrated block should be high. Because as long as a casting sand hole appears in a certain valve hole, the whole integrated block is scrapped.
(2) The stability of machining should be high. Because as long as a certain part is processed out of tolerance, the entire integrated block must also be discarded.
(3) The hardness and wear resistance of the integrated block are better. Now the manifold is mostly made of cast iron, while the valve stem is made of low alloy steel. After heat treatment, the valve stem is generally harder than the valve block. As a result, in use, when damage is caused due to contamination, the valve block is often damaged before the valve stem. The cost of replacing the entire integrated block is obviously much more expensive than replacing the monolithic valve.
Subplate valve: The oil port connecting the pipeline is not directly made on the valve, but on the bottom plate, and the valve is fixed on the bottom plate by bolts. Therefore, it is not necessary to disassemble the pipe when replacing the valve, which is much more convenient than the tube or sheet type, and can greatly reduce the maintenance time and cost. The more important feature of the plate connection method is to lay the foundation stone for the use of manifold connection: multiple plate valves share a connection block - manifold (manifold), and the connection channels between them are made in the block. The total volume is much smaller than the pipe connection. Suitable for more complex hydraulic systems.
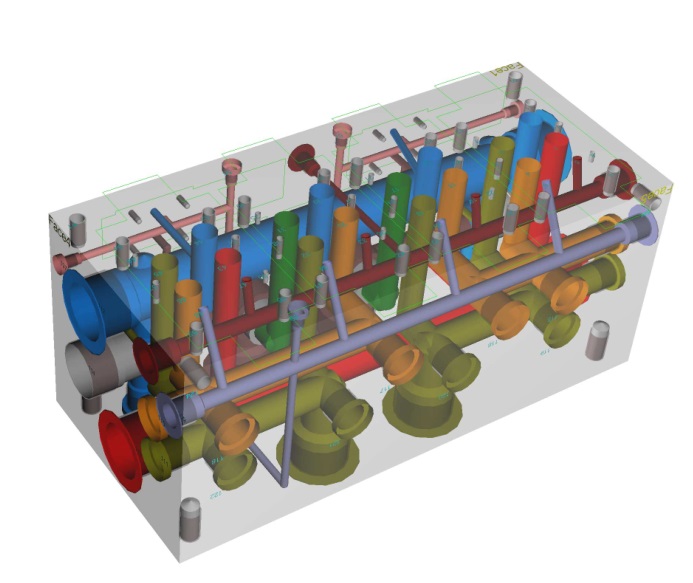
Advantages of Manifolds
In addition to inheriting the advantages of the plate valve - the valve is fixed on the manifold by bolts, so there is no need to disassemble the pipe when replacing - and because the manifold reduces the number of connecting pipes and corresponding pipe joints,
- Potential leakage hazard is reduced;
- the space and weight occupied by the system are reduced;
- The pressure loss of the pipeline is reduced, and the heat generation is also reduced;
- The vibration resistance of the system is increased, and the reliability of the system work is also increased;
- The response time of the system can be significantly shortened;
- Assembly time and costs are reduced;
- Manifolds can be assembled off-site, and the failure rate can be greatly reduced;
- Due to the use of integrated blocks, the control valves are relatively centralized, which is also conducive to maintenance.
Sandwich valve is the extension, expansion and integration of plate valve to height. Typically, a stack controls a set of actuators. It can realize complex functions, is very flexible, and is easy to replace and change. The use of stacked valves can alleviate to some extent the problems of large volume and deep holes encountered in pure plate valve manifolds, but the potential risk of leakage has increased.

Cartridge valves can be regarded as uncoated valves, because they do not have a casing and must be installed in a valve block or manifold to work. Because there is no coat, all the functional parts enter the body of the manifold, so many cartridge valves can be squeezed into a manifold, so it is very compact. The more complex the system, the more prominent this advantage is. Compared with other installation and connection methods, the system composed of cartridge valves is the most compact. Manifolds using cartridge valve inherit all the advantages of plate valve manifolds. And because of the compactness, the volume and weight of the integrated block, and the loss of pressure along the way can be further reduced. The initial cost of the system is reduced due to the compactness, low volume and weight of the integrated block, and the high degree of integration. And due to less possibility of leakage, less pressure loss, less heat generation and high reliability, the operating cost of the whole system can also be reduced. Therefore, the application of in-line valves, plate valves and stack valves has been largely excluded by cartridge valves, especially in-line valves and stack valves.
Cartridges mainly include two types: slip-in and screw-in.


